What is Medicare Tax? How Should Employees and Employers Pay Medicare Tax?
“You are bound to pay Medicare tax in the US if you are a wage earner.”
Yes, the US government imposes a total tax of 2.9% on the employees’ and employers’ wages. The motive of collecting taxes is to help retirees aged 65 and older under the Medicare program.
As a US resident, you should be aware of “what is Medicare tax” to calculate the accurate amount of tax you owe. However, if you are experiencing difficulty in determining withholding rates, you can combine this knowledge with cash flow management services to optimize your finances.
Here, I’ve broken down essential information on what is covered in Medicare insurance, how to pay for it, and much more.
What is Medicare Tax?
Medicare tax is a mandatory federal charge that all employees, employers, and self-employed individuals must pay to the US government’s Medicare program. It is subject to cover the healthcare costs of millions of people.
In other words, the employer withholds the amount from an employee’s paycheck and contributes to healthcare insurance. This insurance facilitates legal US citizens aged 65 and older and young individuals with disabilities. If you are running a small business, accounting services for startups can help track these obligations properly.
Furthermore, the primary purpose of the tax is to fund Medicare Part A, which covers hospital stays, hospice care, nursing home care, and certain other home health services.
What is Covered in Medicare Tax?
The US government Medicare program offers a wider range of facilities separated into Medicare parts A, B, C, and D. These categories include hospital care, nursing facilities, and much more.
The following are the different parts that provide several benefits.
- Medicare Part A:
- Inpatient hospital care
- Skilled nursing facility care
- Hospice
- Some home health care
- Medicare Part B:
- Outpatient care
- Services from doctors and other health care providers
- Durable medical equipment (DME)
- Preventive services
- Medicare Part C:
- Include all the benefits of Part A and Part B.
- Medicare-approved health plans from private companies.
- Additional benefits include routine dental, vision, and hearing care.
- Medicare Part D:
- Provide coverage for prescription medications, which is often offered by private companies.
Businesses and individuals can also integrate bookkeeping services to reconcile these payments efficiently.
How Much Are Medicare Taxes?

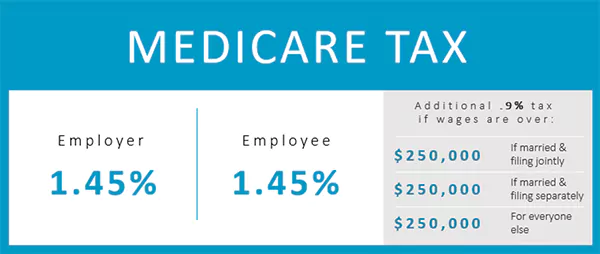
According to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), “The current rate for Medicare is 1.45% for the employer and 1.45% for the employee, or 2.9% total.”
On the other hand, self-employed individuals are subject to paying the full 2.9% Medicare rate. This highlights that the tax contributes 2.9% to the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA), and Social Security covers the rest.
Let’s understand with an example:
An employee earns $1,000 gross wages during a pay period. As an employer, you have to withhold 1.45% from the employee’s paycheck for the Medicare taxes.
It means that you should ($1,000 x 1.45%) $14.5 from an employee’s wages and contribute a matching amount of $14.5 to the Medicare program, according to the IRS rule.
Note: Medicare tax has no wage limit, meaning an employer must continue withholding the amount regardless of what an employee earns.
For accurate reporting and integration into your business’s annual finances, year-end accounts services can help calculate totals and reconcile records.
Also Read: UK Tax Year: A Branded Guide to Stay Compliant with Tax Regulations
What is the Additional Medicare Tax?
On November 26, 2013, the IRS introduced an Additional Medicare Tax (0.9%), which applies to wages payable, self-employed income, and railroad retirement (RRTA) compensation that exceeds certain thresholds.
The following threshold amounts are based on the filing status:
- $250,000 for married filing jointly
- $125,000 for married filing separately
- $200,000 for a single taxpayer.
- $200,000 for a head of household.
- $200,000 for a qualifying surviving spouse with a dependent child.
In order to calculate an employee’s Medicare Surtax, the first $200,000 is subject to the standard Medicare tax rate, and the remaining amount is liable to additional Medicare tax.
Let’s take a look at the following example to learn how to calculate the Medicare Surtax.
A single taxpayer earns $350,000 in 2025. Now, determine the total employee Medicare tax.
Step 1: Standard Medicare Tax
- Tax rate — 1.45%
- Applies to the total salary
Standard Medicare Tax = $350,000 x 1.45%
$5,057
Step 2: Additional Medicare Tax
- Tax rate — 0.9%
- Applies to amounts over $200,000 for single taxpayers.
Additional Medicare Tax = $150,000 x 0.9%
$1,350
Step 3: Total Employee Medicare Tax
Add both tax rates to determine the total amount.
Total Medicare Tax = $5,057 (Standard) + $1,350 (Additional)
$6,425
Overall, an employee is obliged to pay $6,425 to the IRS Medicare program for 2025.
Small business owners or self-employed individuals often pair this knowledge with payroll accounting services to avoid errors and ensure compliance.
Also Read: Purchase Price Variance: Importance, Formula, Examples, Affecting Factors, and Much More
How Do Self-Employed Individuals Pay Medicare Tax?

For self-employed individuals, the Medicare tax rate is 2.9% of total earnings, including both employee and employer contributions.
Significantly, you must pay this tax through the “Self-Employment Tax,” which also covers Social Security. It indicates that the total self-employment tax rate is 15.3%, including 2.9% in Medicare and 12.4% for Social Security.
However, it is important to note that you can calculate the SE tax using Schedule SE, Self-Employment Tax (Form 1040 or 1040-SR). Additionally, you can deduct the employer portion (1.45%) from your tax return when calculating your adjusted gross income.
On the other hand, wage earners or employees cannot reduce Social Security and Medicare taxes. Hence, it is crucial to understand SE rates to file an income tax return and to avoid tax liability.
Also Read: What is the California Exit Tax? How Does the Exit Tax Affect Residents?
The Bottom Line
With the help of the above-mentioned information, you might get an answer to the query, “What is Medicare tax?”
A Medicare tax is an additional charge on individuals who earn wages to fund the US program. The tax is charged on the paychecks and split between the employee and the employer. It aims to provide benefits to senior citizens and persons with disabilities.
So, if you are an employee, the employer should withhold your money to submit to the IRS Medicare program. However, being a self-employed individual, you should pay these surcharges as a Self-employment tax.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: The Medicare tax is used to fund the health system in the United States. It covers hospital insurance for senior citizens and persons with disabilities.
Ans: The total Medicare tax percentage is 2.9%, which is split between the employee and the employer with the same amount of 1.45%.
Ans: Anyone who earns an income in the US should be obliged to pay Medicare tax. Even if the employer and the employee are not citizens of the US, they should also pay taxes.
Ans: No, Medicare tax applies to all your earnings, no matter how high you earn. Plus, high income is subject to the Additional Medicare tax.
Sources: