What is a Schedule E Tax Form? And How to File It?
In the United States, if you have a side income source from rentals, you’re obliged to report it to the IRS. That’s where a Schedule E tax form comes into existence.
It is used to report supplemental income and losses from real estate rentals, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, and trusts. Additionally, you should complete the Sch E tax form along with your main federal tax return, Form 1040.
But you might be confused about how to file it? Don’t fret; I’ve listed detailed guidance on what is a Schedule E tax form, along with its deadlines.
What is a Schedule E Tax Form?

Schedule E tax form is an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) tax form, which records supplemental income and loss through real estate rentals, royalties, or trusts.
You should file it with the IRS along with your Form 1040 to report passive income and expenses. It is one of the various tax forms used to calculate income, credits, and deductions beyond what’s included in Form 1040.
Types of income reported on the Sch E tax form:
- Real Estate Rentals
- Royalties (e.g., oil, gas, copyrights, and patents)
- Partnerships
- S-Corporations
- Trusts and Estates
- Residual income from investment in Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits (REMICs).
Who Fills Out Schedule E Tax Form?

Rental property owners, people who collect royalties, Schedule K-1 recipients, beneficiaries, and investors fill out the Sch E tax form with the IRS.
Let’s take a look at these individuals in great detail.
1. Rental Property Owners
If you rent out some space in your house or other property, income and expenses related to that rental activity are recorded in Schedule E.
However, when you provide services like a cleaning maid to your tenants, the IRS considers it as business income, resulting in you also needing to fill out a Schedule C tax form.
2. People who Collect Royalties
You have to file the tax Schedule E form if you’re collecting royalties as side income that’s not your main job.
For example, if you earn money from a book you published as a side project or oil/gas as an investor, the IRS wants you to report it on the tax form.
3. Schedule K-1 Recipients
In a pass-through entity, the earnings and losses are generally transferred to individuals to pay tax returns as their personal income. So, as a partner or S-corporation shareholder, you’ll receive a K-1 tax form from the entity, which helps you report your individual tax return through the Sch E tax form.
4. Beneficiaries and Investors
If you’re a beneficiary receiving income from estates and trusts, you will get a K-1 that includes your earnings and losses. It guides you in filing the Schedule E tax form.
Moreover, as a REMIC investor, you must use this Schedule form to report your earned income from residual interests for each quarter of the tax year.
Now, skim through the next section to understand how to file Schedule E taxation with step-by-step guidance.
Also Read: What is FITW Tax? Explore Components, Benefits, and Challenges of Federal Income Tax Withholding
How to File Schedule E Tax Form?

Filing out the Schedule E tax form can be a daunting task for you. That’s why I’ve broken down this form into five parts to make it simple and easily recognizable.
Here are the simple steps to learn how to file it.
Part I — Income or Loss From Rental Real Estate and Royalties
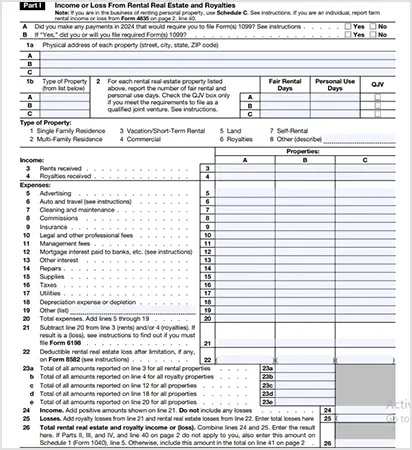
In this section, you will need to fill out the details of the income you earned from rental property and royalties. It includes:
- Physical address of each property
- Types of property
- Report the number of fair rental and personal use days
- Income from rent and royalties
- Expenses, such as advertising, commissions, management fees, etc.
At the end, you need to calculate your gross income and gross loss from rental real estate and royalties.
Part II — Income or Loss From Partnerships and S-Corporations
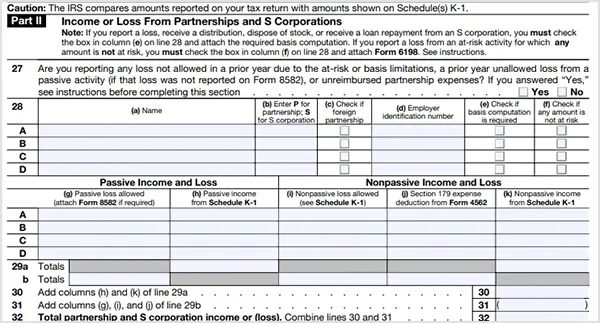
If you are a partner or S-corporation shareholder, you will need several basic details to complete Part II of the Schedule E tax form, such as:
- Name of the entity
- Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Passive income and loss
- Nonpassive income and loss
However, you will need the Schedule K-1 form for filing passive income, nonpassive income, and nonpassive loss. Also, you have to complete Form 8582 if you have passive loss, and Form 4562 in case of Section 179 expense
deduction.
Part III — Income or Loss From Estates and Trusts
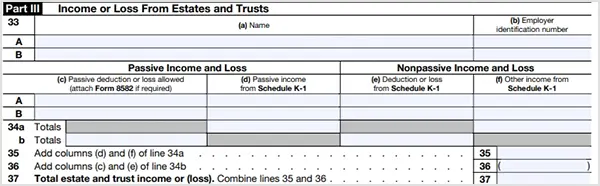
You need to complete this section if you are a beneficiary of a trust or an estate who has earnings and losses to report. The following information is required to fill out Part III:
- Name of the estate or trust
- Employer Identification Number
- Passive income and loss
- Nonpassive income and loss
Similar to Part II, you will need a K-1 and an 8582 tax form to submit details related to income and loss. Lastly, sum up all earnings and losses from estates and trusts.
Part IV — Income or Loss Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits (REMICs) – Residual Holder
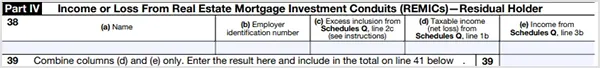
If you are an investor in a real estate mortgage investment conduit (REMICs), you must submit information related to residual interest. Here are the details you need to complete this part:
- Name of the REMIC
- Employer Identification Number
- Excess inclusion, taxable income, or net loss, and income.
The REMIC provides a Schedule Q form that allows you to fill out excess inclusion, taxable income, or net loss, and income.
Part V — Summary
In the last section, you must sum up your income and losses from all the previous sections (in case you’re eligible for multiple sections). However, special sections like farming and fishing income, and real estate professionals are only filed by eligible taxpayers. Hence, you should avoid these considerations while submitting the Schedule E.
Also Read: What is an Ad Valorem Tax? Definition, Reporting, and How It Is Assessed
When Should You File Schedule E Tax Form?

You should file the Schedule E tax form with your primary tax return, i.e., Form 1040, by the mid-April (15 April) deadline or mid-October with an extension.
However, if you’re a partner or shareholder in an S corporation, you will get the Schedule K-1 around mid-March. As a result, you might have pressure to fill out the form in a limited time.
On the other hand, if you file Form 4868, you could automatically get an extension of time. It is important to note that the extension only pushes out the deadline, not the pay.
Remember, if you have a tax bill and forget to pay by the deadline, you could end up with some interest and penalties during the process, increasing your tax liability.
What is the Difference Between Schedule C and E?
In short, Schedule C is for reporting active income as a sole proprietor and single-member LLC. On the other hand, Schedule E reports passive income from real estate and investments.
Let’s take a look at the breakdown table representing the difference between Schedule C and E.
| Basis | Schedule E | Schedule C |
| Type of Income | Passive income: It reports supplemental income and loss from real estate, royalties, and natural resources as side earnings. | Active income: It reports profits and losses from a business where you’re actively involved. |
| Real Estate | If you rent out some portion of your home or other property, it is reported in the Sch E tax form. | If your real estate activity is a business, you should file a Schedule C tax form for your tax return. |
| Self-Employment Taxes | Passive income is generally not subject to self-employment taxes. | Profits are subject to self-employment taxes (Social Security and Medicare). |
| Loss Limitations | Passive business losses are only used to deduct passive income. | Active business losses can be used to deduct income on your tax return, such as wages. |
Also Read: Biweekly Pay: Learn How to Calculate Biweekly Pay, Along with Its Advantages and Challenges
The Bottom Line
With the above information, I hope you understand what is a Schedule E tax form. It is an IRS tax form used to file your tax return on supplemental income or loss.
In simple words, if you have a side income from real estate rentals, royalties, or investments in REMIC, you’re obliged to file a Schedule E tax form by the deadline.
However, filing this form can be a baffling topic for you as a beginner, so I advised you to opt for outsourcing tax professionals to avoid discrepancies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: Schedule E is an IRS tax form used to report income and losses from rental real estate, partnerships, and S corporations.
Ans: Yes, you can deduct property taxes from a rental property on Schedule E. Unlike the property tax deduction for a personal residence, there is no $10,000 limit on deductions.
Ans: Yes, you can file Schedule E online along with Form 1040 as a part of your federal tax return.
Ans: Schedule E is submitted annually by the mid-April tax deadline, or by mid-October if you file an extension.
Sources: