Retained Earnings: Explanation, Formula, and Importance for Businesses
Profit and revenue are the main variables that pop up when you measure a company’s growth. However, a key factor that leads the way but is often overlooked is retained earnings. People frequently overlook its importance, but it contributes highly to growth— especially when aligned with accounting service for startup principles.
Poor management of earned surplus due to not opting for corporate accounting. Ever seen a company shut down even after having good revenue and profits? All this is because of poor management of earned surplus due to not opting for corporate accounting. It is the accounting concept that needs to be deeply studied for the active growth of businesses, similar to how bookkeeping services ensure structured record-keeping.
Therefore, we’ll break down the concept of retained earnings, its formula, its importance, and how to find it. Grab a pen and paper and take notes while reading!
What are Retained Earnings?
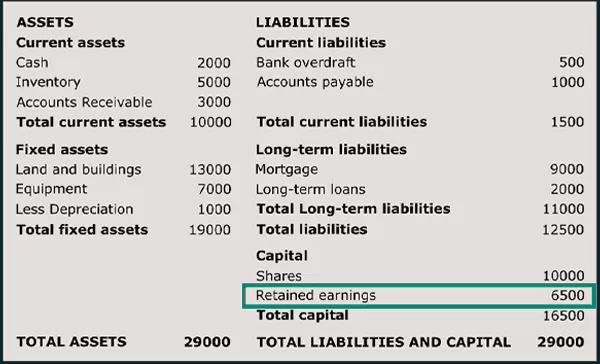
Retained earnings are a portion of money every business keeps aside to fund its future goals, like product development and scaling. They aren’t given out as dividends to the shareholders and come directly from the business’s earnings channels.
As the amount is reinvested into the business, you can call it an internal savings account where the money accumulates over time. This is a part of the bookkeeping that is displayed under shareholders’ equity in the balance sheet and is audited every year for financial planning. Businesses often analyze this figure alongside the accounting equation to maintain balance.
In simple terms, you can say that Retained Earnings = Net Profit – Dividends Paid.
Now that you’re introduced to the retained earnings definition, let’s go ahead and understand its formula.
How to Calculate Retained Earnings?

The retained earnings are calculated based on the retained earnings equation, i.e.,
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends
Where,
- Beginning Retained Earnings = Amount of retained earnings accumulated over the previous period.
- Net Income = Total profit that the business has earned, subtracting the expenses.
- Dividends = The portion of profit that goes straight to shareholders.
Let’s use the retained profit formula as an example to understand it better.
A brick manufacturing company, TurboRocks Ltd., has begun with accumulated profits of $200,000. In the year 2024, their revenue was $500,000, and total expenses, including salaries, rent, materials, etc., were $350,000.
Their net income is $150,000 (Revenue — Expenses).
Dividends that need to be paid are $40,000.
Using the retained earnings equation, here’s how to find the numbers for TurboRocks Ltd.:
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends
Retained Earnings = $200,000 + $150,000 – $40,000
= $310,000
This means they will have $310,000 as retained earnings in their account at the year-end — a figure often reconciled during year-end accounts services.
What is the Need for Keeping Retained Earnings?
Companies use the retained earnings equation religiously every year. Here are the reasons why:
- Scaling Purposes: Expansion or scaling a business requires capital. Whether you want to open a new branch, enter new markets, or launch new products, all of this asks for a significant amount to be spent. Retained earnings offer an easily accessible funding source without taking loans or diluting equity.
- Research and Development: This plays a very important role before launching a business or even every product in the market. The R&D process helps to position the business, mark out the requirements of people, find the target audience, and all the nitty-gritty. All of this takes a lot of money, and if you have retained earnings, you can use them to fuel this process — similar to how strategic cash flow management supports long-term planning.
- Paying Off Debt: It is normal for businesses to take loans and external monetary help. To pay back the loan, they can use the retained profit formula, which helps to create debt management strategies for improving their financial health and standing.
- Stand Up During Economic Downturns: Recessions and pandemics cause economic downturns that are beyond imagination. As the markets shut down, the companies go through tough times and can end up taking loans. If the business has retained earnings, it can stand still even in distressed times.
- Buying Back Stocks: Retained profits can be used to buy back the company’s shares. This potentially raises stock value and increases ownership stakes for existing shareholders.
Check Out: Payslips Explained: Components, Importance, and Everything You Must Know About
Factors Affecting Retained Earnings
Having retained earnings serves as a cushion against the storms for businesses. However, it can fluctuate too, as it is dependent on many factors that you must know about.
- Net Income or Net Loss: This is the main deciding factor for the retained earnings. When the company earns more profit, the RE increases; if it incurs a loss, the RE drops.
- Dividend Payments: Wherever the business pays out dividends, it takes a portion away that can not be reinvested. It just distributes the profits, and it can increase or decrease depending on the amount to be paid.
- Changes in Accounting Policies: The companies may reevaluate their accounting policies to adjust their profits and losses. This can either work in favor, increasing accumulated profits, or the opposite. These changes often correlate with differences in accounts payable vs accounts receivable strategies.
- Growth and Expansion Needs: The companies having an aggressive expansion plan will need more retained earnings compared to those in the stable or low expansion phase.
Limitations of Retained Earnings
Even though retained earnings are valuable for companies, there are still limitations to them that you must know about. Here are some drawbacks that come with accumulated profits:
- Not Available in Liquid: Retained earnings are considered to be cash on hand. However, it basically consists of non-liquid assets or investments, such as fixed deposits or real estate. This indicates that a company could have a high-earned surplus but still encounter cash flow challenges — which is why reviewing a cash flow statement is essential.
- No Info About Business Performance: The retained earnings do not directly tell about the business performance. This means that having high accumulated profits in the account does not always mean the company is profitable.
- Shows Lack of Capital Management: The companies that have excessive RE may have poor capital management. They are either not reinvesting wisely or not paying timely to the shareholders. This signals that the company may be in trouble and needs a clear budgeting strategy.
- Uncertainty in Future Returns: Having investments via RE does not mean you will reap profits in the future. Poor capital allocation, decision-making, and economic troubles may lead to losses.
How Retained Earnings Impact Shareholders?
The retained earnings definition explains that it is part of an accounting system that directly or indirectly impacts the shareholders. Let’s understand:
- Dividend Payouts: Shareholders gain a significant amount of dividends with every profit cycle. The companies having high RE may think of reinvesting the money rather than paying off dividends. This can cause strain on the relationship between future-focused owners and income-focused investors.
- Capital Appreciation: Retained earnings are used for market expansion, new product launches, and upgrades. If the investment works in its favor, it can boost profitability and competitiveness, increasing the value of the stock. And over time, the shareholders can enjoy capital gains.
- Management Strategy: Shareholders can evaluate if management is concentrating on rapid growth, preserving financial reserves, or providing returns to investors via dividends. A growth-focused investor may favor businesses that keep earnings for expansion, whereas income-focused investors might choose companies that reliably share profits. This consideration is grounded in core principles like the accounting equation.
Retained earnings can help the shareholders earn a fortune in the future if they value growth and can even cause trouble if the management strategy is not clear.
So this was all about retained earnings, its equation, examples, affecting factors, limitations, and how to find it. We hope this blog has helped you understand the concept and will help you make wise decisions in calculating retained capital for your company.
Read Next: Tax Accounting: Definition, Types, Importance, Methods, and Effective Steps to Calculate
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: No, retained earnings are not an asset. This comes under shareholder’s equity and represents the net income the company has kept for future use.
Ans: Yes, the company makes more losses or pays out more dividends than the money it holds, which can show negative retained earnings over time.
Ans: No, shareholders do not get retained earnings directly. They can only benefit from an increase in stock value and dividends.
Sources